Surprising benefits of a good sleep
A good night's sleep is incredibly important for your health.
In fact, it’s just as important as eating healthy and exercising.
Unfortunately, the Western environment is interfering with natural sleep patterns.
People are now sleeping less than they did in the past, and sleep quality has decreased as well.
Here are 5 reasons why good sleep is important.
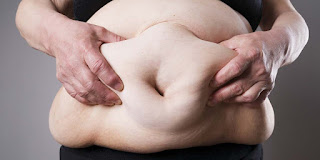
1. Poor Sleep Can Make You Fat
Poor sleep is strongly linked to weight gain.
Short sleep duration is associated with a drastically increased risk of weight gain and obesity, in both children and adults.
Studies show that sleep-deprived individuals have a bigger appetite and tend to eat more calories.
Poor sleep affects hormones that regulate appetite. Those who get adequate sleep tend to eat fewer calories than those who don't.

2. Good Sleep Can Improve Concentration and Productivity
Sleep is important for various aspects of brain function.
All of these are negatively affected by sleep deprivation.
Good sleep can maximize problem-solving skills and enhance memory. Poor sleep has been shown to impair brain function.
Mental health issues, such as depression, are strongly linked to poor sleep quality and sleeping disorders.
3. Good Sleep Can Maximize Athletic Performance
Sleep has been shown to enhance athletic performance.
In a study on basketball players, longer sleep was shown to significantly improve speed, accuracy, reaction times and mental wellbeing.
Longer sleep has been shown to improve many aspects of athletic and physical performance.

4. Poor Sleepers Have a Greater Risk of Diseases
It’s known that sleep quality and duration can have a major effect on many health risk factors.
These are the factors believed to drive chronic diseases, including heart disease.
A review of 15 studies found that people who don’t get enough sleep are at far greater risk of heart disease or stroke than those who sleep 7–8 hours per night
Sleeping less than 7–8 hours per night is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Experimental sleep restriction affects blood sugar and reduces insulin sensitivity
.
Poor sleep habits are also strongly linked to adverse effects on blood sugar in the general population.
Those sleeping less than six hours per night have repeatedly been shown to be at an increased risk of type 2 diabetes
Even a small loss of sleep has been shown to impair immune function
One large two-week study monitored the development of the common cold after giving people nasal drops with the cold virus
They found that those who slept less than seven hours were almost three times more likely to develop a cold than those who slept eight hours or more.
If you often get colds, ensuring that you get at least eight hours of sleep per night could be very helpful. Eating more garlic can help as well.
5. Sleep Affects Emotions and Social Interactions
Sleep loss reduces your ability to interact socially.
Several studies confirmed this using emotional facial recognition tests.
One study found that people who had not slept had a reduced ability to recognize expressions of anger and happiness
Researchers believe that poor sleep affects your ability to recognize important social cues and process emotional information.


0 Comments